Carbon Capture and Storage( CCS) A pivotal Tool in the Fight Against Climate Change
Introduction
As the world grapples with the critical need to reduce hothouse gas emigrations and alleviate climate change, innovative technologies similar ascarbon capture and Storage( CCS) have surfaced as pivotal tools in the magazine of climate results.
CCS involves landingcarbon capture and sequestration dioxide( CO2) emigrations from artificial processes or power shops, transporting it to storehouse spots, and securely storing it underground to help its release into the atmosphere.
This composition explores the conception of CCS, its implicit benefits and challenges, current operations, and its part in shaping a sustainable future.
Understanding Carbon Capture and Storage( CCS)
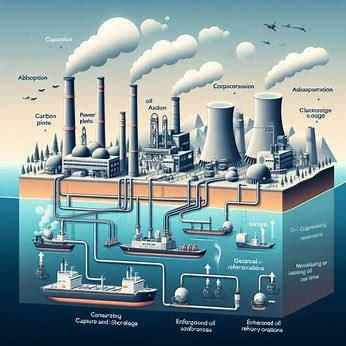
carbon capture and storage technology ( CCS) is a process designed to alleviate climate change by landing CO2 emigrations from artificial sources similar as power shops, cement manufactories, and refineries before they're released into the atmosphere.
The captured CO2 is also transported via channels or vessels to suitable storehouse spots, generally deep underground geological conformations similar as depleted oil painting and gas budgets, saline aquifers, or unmineable coal seams.
Once stored underground, the CO2 is securely trapped, precluding its release and effectively reducing the net emigrations from the source.
ccs carbon can be stationed using different technologies, includingpost-combustion prisoner,pre-combustion prisoner, and oxy- energy combustion.
Post-combustion prisoner involves landing CO2 from the stovepipe feasts emitted by artificial processes using chemical detergents or sorbents. Pre-combustion prisoner entails converting fossil energies into syngas( a admixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide) before combustion, allowing for the separation and prisoner of CO2.
Oxy- energy combustion involves burning fossil energies in oxygen-rich surroundings, performing in stovepipe feasts with high attention of CO2 that can be fluently captured.
Benefits of Carbon Capture and Storage( CCS)
1. Emission Reduction CCS enables significant reductions in CO2 emigrations from artificial sources, helping to meet emigrations targets and combat climate change.
By landing and storing CO2 that would else be released into the atmosphere, CCS facilitates the decarbonization of sectors similar as power generation, cement product, and sword manufacturing.
2. Climate Mitigation CCS plays a pivotal part in achieving climate mitigation pretensions by enabling the continued use of fossil energies while minimizing their environmental impact.
It provides a ground to a low- carbon future by allowing for the gradational transition to renewable energy sources while icing energy security and affordability in the interim.
3. Enhanced Energy Security CCS can contribute to energy security by conserving the part of fossil energies in the global energy blend while reducing their environmental footmark.
By landing CO2 emigrations from being reactionary energy structure, CCS helps to extend the lifetime of these means while easing the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid.
4. Economic openings The deployment of CCS presents openings for profitable growth and job creation, particularly in regions with abundant reactionary energy reserves.
carbon capture storage technologystructure systems bear professed labor and moxie in engineering, construction, and operations, generating employment openings and stimulating original husbandry.
Challenges and walls to Deployment
Despite its implicit benefits, the wide deployment of CCS faces several challenges and walls
1. Cost The high capital and operating costs associated with CCS technology remain a significant hedge to its wide relinquishment.
The construction of CO2 prisoner installations, transportation structure, and storehouse spots requires substantial investment, making CCS systems economically challenging without sufficient fiscal impulses or nonsupervisory support.
2. Regulatory and Policy query The lack of clear nonsupervisory fabrics and policy impulses for CCS deployment hinders investment and design development.
query regarding carbon pricing mechanisms, emigrations trading schemes, and liability for stored CO2 complicates decision- timber and undermines investor confidence.
3. Public Acceptance and Stakeholder Engagement Public perception and acceptance of CCS systems can vary depending on factors similar as environmental impacts, safety enterprises, and community engagement.
Addressing public misconceptions and engaging stakeholders in the planning and perpetration of CCS enterprise are essential for erecting trust and fostering social license to operate.
4. Specialized and Geographical Constraints The vacuity of suitable storehouse spots, geological characteristics, and propinquity to emigration sources pose specialized and logistical challenges for CCS deployment.
relating and assessing suitable storehouse budgets, icing geological integrity, and minimizing leakage pitfalls are critical considerations in point selection and design planning.
Current operations and unborn Outlook
Despite the challenges, CCS technology is formerly being stationed in colorful regions around the world, with notable systems in North America, Europe, and Asia.
In the United States, the Petra Nova design in Texas and the Illinois Industrial CCS design are introducing CCS deployment in the power generation and artificial sectors, independently.
In Europe, the Northern Lights design in Norway aims to establish a CCS structure for the transportation and storehouse of CO2 captured from artificial installations across Europe.
Looking ahead, the future of CCS hinges on cooperative sweats between governments, assiduity stakeholders, and exploration institutions to address specialized, profitable, and nonsupervisory challenges.
Policy support, fiscal impulses, and transnational cooperation are essential for accelerating CCS deployment and scaling up its impact on emigrations reduction.
Advances in CCS technology, including the development of new prisoner ways, bettered storehouse monitoring technologies, and enhanced geological modeling, will further enhance the effectiveness and cost- effectiveness of CCS systems.
Conclusion
Carbon Capture and Storage( CCS) holds immense pledge as a vital tool in the global trouble to combat climate change and transition to a low- carbon frugality.
By enabling the prisoner and storehouse of CO2 emigrations from artificial sources, CCS offers a realistic result to reduce hothouse gas emigrations while maintaining energy security and supporting profitable growth.
Despite the challenges and walls to deployment, continued invention, policy support, and transnational collaboration can unleash the full eventuality of CCS and pave the way for a sustainable future.
▻carbon capture and sequestration
▻carbon capture
▻carbon capture and storage technology
▻carbon capture storage
▻ccs carbon
▻ccs carbon capture storage
▻carbon capture storage technology
Some related post
next generation Battery-operated
YOU MIGHT LIKE
SOME POPULAR POST
Twitter-X Elon Musk Content Moderation
Tesla Cybertruck Crash in Palo Alto
► Official Web▼
▻https://www.techlzosh.info/
► Contact▼
IF YOU HAVE ANY PROBLEMS SO COMMENT ME I REPLAY YOU FAST
share this post


.jpeg)
.jpeg)

.jpeg)

.png)


.jpeg)






.png)
0 Comments